- July 10, 2020
- Posted by: Nguyen Manh
- Category: Accounting

Service of preparing Customs Finalization Report
Customs Finalization report forms must be submitted according to Circular 39:
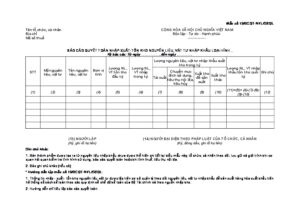
Form 15 Final settlement report with imported raw materials
Form 15a Final settlement report for exported finished products
Form 16 Actual usage norms
Raw materials and supplies imported for processing and production of exported goods and export-processed goods include:
- Raw materials, semi-finished products, components, and component assemblies directly participate in the processing and production process to constitute export products.
- Raw materials and supplies directly participate in the processing and production of export products but are not directly transformed into products or do not constitute product entities.
- Finished products imported by organizations or individuals to be attached to export products, to be packed together with export products made from imported raw materials and supplies, or to be packed together with export products manufactured exported from domestically purchased raw materials and supplies, self-supplied raw materials and supplies into synchronized products for export abroad.
- Packaging materials or packaging for packaging export products.
- Raw materials and supplies imported for warranty, repair, and recycling of exported products.
- Imported sample goods for processing and production of exported goods.
Actual norms for processing and manufacturing export products
- Actual norms for processing and manufacturing export products include:
- a) Raw material usage norm is the necessary and actual amount of raw materials used to produce one unit of product;
- b) The norm of consumable materials is the actual amount of consumable materials to produce one unit of product;
- c) The rate of loss of raw materials or supplies is the actual amount of raw materials or supplies lost, including natural loss, loss due to scrap and waste products calculated at the rate of % compared to the actual norm. production or compared to raw material usage norms or consumable supplies norms. In case the amount of scrap and waste products is included in the usage norms or norms of consumable materials, it is not included in the rate of loss of raw materials or supplies.
Raw material usage norms, consumable supplies norms and loss rates of raw materials and supplies are kept at the enterprise and presented when customs authorities inspect or request explanations on how to calculate norms and ratios. loss of raw materials and supplies.
- The norm of separating raw materials from starting materials is the amount of raw materials used to produce exported products separated from one starting material.
- Before carrying out production, organizations and individuals must establish usage norms and expected loss rates for each product code. During the production process, if there is a change, the actual norm must be rebuilt and documents related to the norm change must be kept.
- The legal representative of the organization or individual is responsible for the accuracy of usage norms, consumption norms, loss rates and using the norms for the correct purpose of processing and producing goods. export; Violations will be handled according to the provisions of law.
- When determining the amount of tax to be refunded or not collected, organizations and individuals shall base themselves on the provisions of this Circular and the actual norms of using imported raw materials and supplies to produce export products.
Deadline for submitting customs settlement reports
Organizations and individuals submit final settlement reports on the use of exported raw materials and supplies to produce processed goods abroad or at EPEs no later than the 90th day from the end of the fiscal year or Before carrying out the consolidation, merger, separation, or dissolution, send it to the Customs Branch where the processing contract has been notified.
Check the use and inventory of raw materials, supplies, machinery, equipment and exported goods
- Test cases
- a) When determining that an organization or individual showing signs of risk has imported machinery, equipment, and raw materials but has passed the production cycle without exporting products;
- b) When there are signs that organizations or individuals importing raw materials, supplies, machinery, equipment or exporting products have abnormally increased or decreased compared to production capacity;
- c) When there are signs identifying organizations or individuals selling raw materials, supplies, machinery, equipment, and products into the inland but not declaring customs;
- d) When detecting organizations or individuals declaring exported products incorrectly according to regulations and reality.
test content
- a) Check customs documents, tax refund and non-collection documents (in case of combining inspection of tax refund and tax non-collection documents), finalization reports, accounting documents, accounting books, Documents tracking raw materials, supplies, machinery, equipment imported and exported, and other documents that customs declarants must keep according to the provisions of Clause 5, Article 3 of this Circular;
- b) Check the actual norms of exported products and documents related to the establishment of norms;
- c) Check the compatibility of exported products with imported raw materials and supplies;
- d) In case through inspection of the contents specified in Points a, b, c of this Clause, the customs authority detects signs of violation but does not have enough basis to conclude, then:
d.1) Check raw materials, supplies, machinery and equipment on the production line;
d.2) Check the quantity of goods remaining in the warehouse;
d.3) Check the quantity of finished products that have not yet been exported.

Test time
The inspection is carried out no more than 05 working days at the production facility or headquarters of the organization or individual. For complicated cases, the Director of the Customs Department shall issue a decision to extend the inspection deadline but not to exceed 5 working days.
Is your business having difficulty preparing customs settlement reports?
Late submission of customs finalization report
Data discrepancies between accounting and the import-export department lead to tax arrears
Enterprises do not clearly understand the declaration and use of imported raw materials and supplies to produce export goods
The settlement report has unusual discrepancies in data compared to the Customs system, leading to fines
Enterprises have not updated old and new customs procedures
According to high requirements for internal corporate governance.
With experience in customs inspection consulting and customs settlement report preparation services for many businesses, AACS Company understands the difficulties of import-export and processing businesses in preparing settlement reports. Custom.
Therefore, we at AACS have experience in the field of Accounting and Auditing combined with data processing to provide Customs settlement reporting services for customers.
When you use AACS's Customs Finalization Report service, we will share the following issues with you:
+ How to set up each target for final settlement report. How to handle data differences. How to account for and maintain the cost of imported raw materials and supplies.
+ Experience in controlling production materials. The way to calculate input materials is not tracked separately.
+ Regulations on handling scrap and waste within norms and outside norms. Points to note when customs authorities check reports. Preparation work before the customs authority checks the report. How to set each target in the export production settlement report.
+ How to set each indicator in the final settlement report of processed goods
To receive a quote for preparing a Customs Finalization Report, please contact AACS:
Phone: 028 66 500 381 – 0908 381 550 (Mr Manh)
Email: manhnd@aacs.com.vn
See more: Content of Customs Inspection consultation
